3D printing is an additive process that builds objects layer by layer from a digital model. It can create intricate structures that are difficult or impossible with traditional methods. In the architecture field, practitioners can use 3D printing to create detailed scale models and unique structural features efficiently.
In this article, we explore the transformative role of 3D printing in architecture, delving into its advantages, challenges, and the future it holds for the industry.
Pros of 3D Printing in Architecture
Architects are increasingly engaging 3D printing services to improve their work processes. It also has become an affordable yet powerful toolkit that enhances their capabilities and fosters innovation. 3D printing offers several distinct advantages for architects, including:
Rapid Prototyping: Allows architects to quickly create physical prototypes, fostering innovation and iterative design processes.
Customization and Personalisation: Offers unique opportunities for creating customised architectural elements, enhancing personalization in design.
Reduced Construction Time and Costs: Streamlines construction processes, reducing labour costs and material waste, and promoting sustainable building practices.
Cons of 3D Printing in Architecture
Despite its outstanding benefits and features, 3D printing in architecture, as with any emerging technology, also faces certain limitations and challenges that need to be considered.
High Costs: Initial investment in 3D printing equipment can be substantial, posing a challenge for small businesses or individual architects.
Skilled Labour Shortage: The industry faces a lack of trained professionals adept in 3D printing technology, impacting its wider adoption.
3D Printing in Architecture 2024
In 2024, 3D printing in architecture is revolutionising design with sustainable practices, complex geometries, cost-effective urban solutions, heritage conservation, and customised spaces, while integrating smart technology and fostering educational collaboration.
Architects are creatively utilising the technology in their daily workflow, particularly in prototyping, pitching design ideas, and improving overall efficiency.
Prototyping
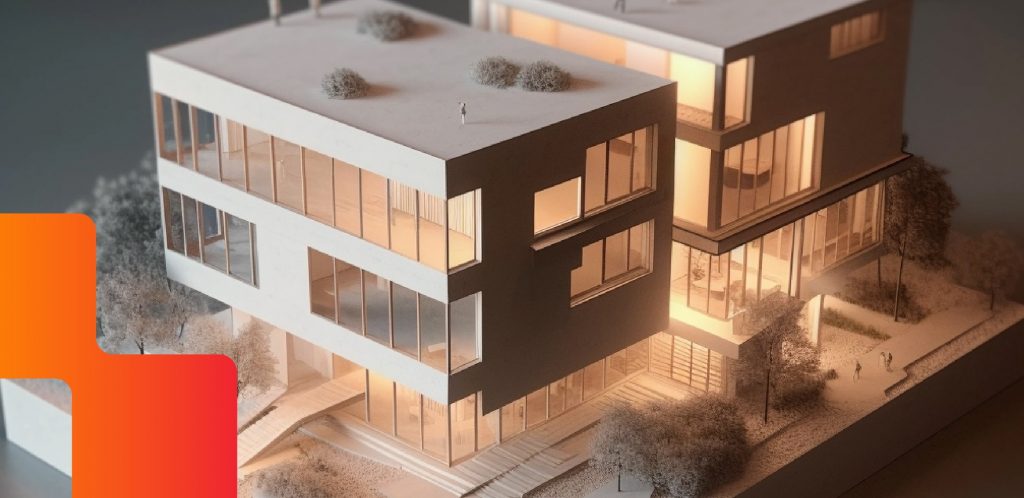

3D printing is widely used to create physical models of architectural designs. Unlike traditional two-dimensional representations, such as blueprints and drawings, 3D-printed models provide a realistic, three-dimensional representation of the proposed structure. These models allow architects to visualise and understand more about the design before actual construction, such as this 3D-printed neighbourhood in Texas.
Pitching Ideas
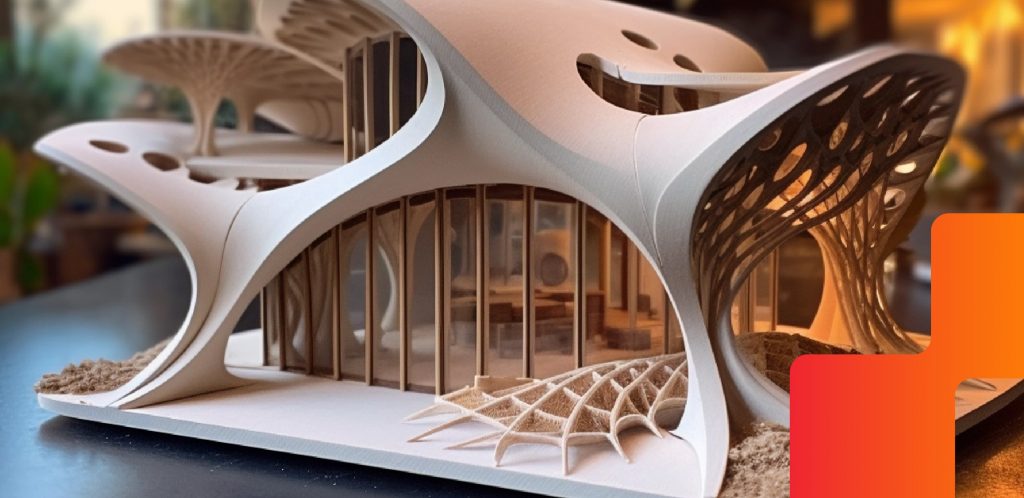

Improving Workflow Efficiency
In addition to showcasing overall design concepts, 3D printing can be employed to highlight specific design elements and intricate details, transforming pitches from mere presentations into immersive experiences. From showcasing innovative structural components to demonstrating unique material finishes, 3D-printed models provide a level of detail that cannot be captured by digital presentations.
3D printing enables rapid prototyping, allowing architects to quickly create physical models of their designs. This facilitates iterative design processes, where architects can swiftly visualise, evaluate, and refine their designs based on feedback from clients. 3D-printed models optimise construction planning by providing precise structural detail which minimises delays and reduces waste.
Choosing 3D Printers for Architecture
A variety of 3D printing technologies are available for creating architectural models, each with its own strengths and limitations. These specialised printers offer a multitude of benefits that enhance the design process, elevate project outcomes, and promote sustainability in architecture. Some of the most commonly used technologies include:
Filament-Based Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM is a versatile and affordable technology that uses plastic filaments to create models layer by layer. It is particularly well-suited for creating large-scale models.
Resin-Based Stereolithography (SLA): SLA produces highly detailed and accurate models with a smooth surface finish. It is ideal for creating intricate models with fine details.
Powder-Based Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS uses a laser to sinter fine particles of powder, creating strong and durable models. It is often used for creating models that require structural integrity.
Binder Jetting : Binder jetting offers several distinct advantages for architects, making it a compelling choice for creating architectural models, prototypes, and even full-scale structures:
Keys Takeaways
As 3D printing technology continues to mature and its applications expand, it is expected to play an increasingly significant role in shaping the future of architecture. Moreover, 3D printing has the potential to transform architectural practices, enabling more efficient, sustainable, and high-quality projects.
By enabling on-site fabrication, minimising material waste, and optimising structural integrity, 3D printing in architecture has the potential to reduce construction costs, minimise environmental impact, and enhance the durability of buildings.
If you are interested in leveraging 3D printing but don’t know how or where to start, check out R3DPrints as they are one of the most renowned experts in this field.