From the pages of magazines to the dynamic world of virtual reality, the interplay between graphic design and 3D modeling is redefining the boundaries of artistic expression and viewer engagement.
While similar, the two disciplines are actually distinct in purpose, skill sets, and tools used. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between graphic design vs 3D modeling, as well as which is the most suited for your needs.
Graphic Design vs 3D Modeling
Graphic design focuses on 2D visual communication using tools like Adobe Creative Suite. In contrast, 3D modeling creates 3D digital objects with software such as Blender.
Purpose and Scope
Both disciplines utilize visual elements to convey messages, evoke emotions, and create engaging experiences. However, they serve different purposes.
| Graphic Design | 3D Modeling |
| Primarily focuses on creating two-dimensional visual elements for various applications, including print media, digital platforms, and branding. | Concentrates on crafting three-dimensional digital representations of objects or environments, primarily utilized in product design, architecture, and animation. |
Software and Tools
Graphic design and 3D modeling both rely on specialized software tools to bring their creative visions to life. These tools allow them to manipulate and combine visual elements to create impactful designs.
| Graphic Design | 3D Modeling |
| Employs software like Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign, emphasizing image editing, typography, and layout. | Relies on specialized software like Blender, Maya, and 3ds Max, focusing on creating, manipulating, and rendering 3D models. |
Visual Aesthetics
Both graphic design and 3D modeling employ their unique aesthetic approaches to enhance visual storytelling, product visualization, and creative expression. The choice of aesthetic depends on the specific project’s goals and the desired impact on the viewer.
| Graphic Design | 3D Modeling |
| Emphasizes two-dimensional elements, including shapes, colors, typography, and imagery, to convey messages and evoke emotions. | Explores depth and realism, utilising lighting, textures, and materials to create lifelike representations of objects and environments. |
Skill Sets Required
The specific skill sets required for each discipline vary depending on the project’s complexity and the desired outcome. However, both graphic design and 3D modeling demand a blend of artistic sensibility and technical proficiency to bring creative visions to life.
| Graphic Design | 3D Modeling |
| Demands strong visual communication skills, an understanding of color theory and typography, and proficiency in design software. | Requires a blend of artistic and technical skills, including knowledge of 3D modeling software, understanding of geometry and perspective, and attention to detail. |
Learning Curve and Pathways
Graphic design and 3D modeling, both rooted in visual communication, offer diverse creative avenues yet present varying learning curves and pathways to mastery.
| Graphic Design | 3D Modeling |
| Typically requires a formal education in graphic design or a related field, with a focus on design principles, software training, and portfolio development. | Can be pursued through self-study, online courses, or specialized programs, with a focus on mastering 3D modeling software, understanding 3D modeling techniques, and building a portfolio. |
Pros and Cons of Graphic Design and 3D Modeling
Though both graphic design and 3d modeling are different in their own ways, it’s also crucial to learn about their pros and cons to gain a comprehensive understanding of the dynamic landscape within graphic design and 3D modeling.
Graphic Design
| Pros | Cons |
| Versatile: Graphic design can be used for a wide variety of purposes, including print, digital, and branding applications. | Competitive: The graphic design industry is very competitive, so it can be difficult to get started. |
| Ability to be creative :Graphic designers are constantly engaged in a creative process, regularly exploring new ideas and experimenting with design concepts. | Long hours: Graphic designers often work long hours, especially when deadlines are looming. |
| In-demand: Graphic designers are in high demand across a variety of industries. | Stressful: Graphic design can be a stressful job, especially when dealing with clients and deadlines. |
3D Modeling
| Pros | Cons |
| Realistic: 3D modeling can create incredibly realistic and lifelike representations of objects and environments. | Technical: 3D modeling can be technically challenging, requiring a strong understanding of software and geometry. |
| Saves production time : 3D models offer remarkable flexibility and efficiency in production, enabling rapid prototyping which leads to faster and more efficient production. | Time-consuming: 3D modeling can be time-consuming, especially for complex projects. |
| Improves design accuracy : 3D modeling enhances precision in design by ensuring meticulous accuracy in every detail, guaranteeing that what is represented in the model is precisely what will be constructed or produced. | High-end hardware: For optimal performance, 3D modeling software typically requires high-performance computers equipped with advanced graphics capabilities. |
Graphic Design or 3D Modeling: Specific Applications
3D Printing Enthusiasts and Professionals

3D modeling is essential for creating detailed prototypes of new product designs, custom components for machinery, or intricate parts for model-making. For example, an engineer might use 3D modeling to design and print a custom drone part, while graphic design could be used to create the branding and instructional materials for the product.
Corporations

Corporations can use 3D modeling to design unique trophies shaped like their logo or products, offering a personalized touch for corporate events or recognition awards. Graphic design complements this by creating the packaging design, event invitations, and branding materials that accompany these trophies, ensuring a consistent and professional corporate image.
Architects
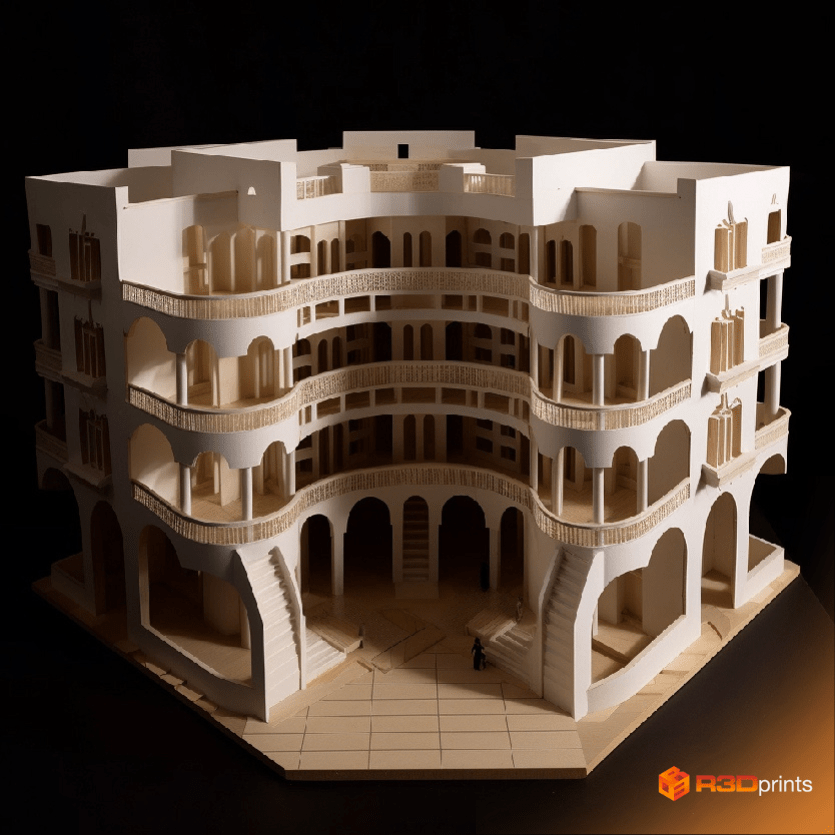
In architecture, 3D modeling is crucial for building detailed scale models of buildings or urban planning projects, providing a tangible representation for clients and stakeholders. Additionally, graphic design can be employed to produce visually appealing project presentations, site boards, and marketing brochures that highlight the features and aesthetics of the architectural design.
Artists
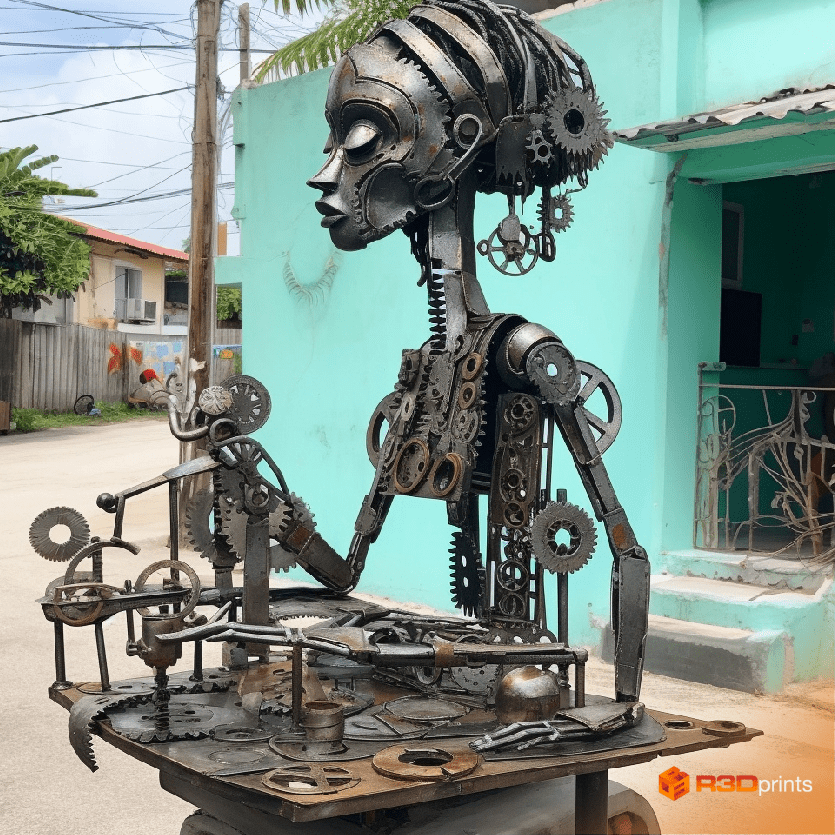
Artists can leverage 3D modeling to experiment with complex sculptural forms that might be challenging to execute in traditional mediums. For instance, a sculptor could create a digitally-designed installation piece that intertwines organic and geometric shapes. In parallel, graphic design can be used to develop exhibition layouts, promotional posters, and digital portfolios that showcase the artwork effectively.
Key Takeaways
Graphic design and 3D modeling, while sharing common goals in visual communication, diverge in their learning curves and pathways. Graphic design requires a formal education and hands-on experience, while 3D modeling offers flexibility in self-study or specialized programs.
The experts in this field will guide you through the intricacies of each discipline, equipping you with the skills and knowledge to transform your creative visions into reality. Contact R3DPrints today to harness the power of 3D modeling and bring your creative vision to life.

